Overview
Use PeakUtils to find peaks in a graph. For more informations about different peaks implementations, see https://blog.ytotech.com/2015/11/01/findpeaks-in-python.
Update 2019-04-11: A better way to find peaks is to use scipy.signal.argrelextrema() function.
Requirement
apple.csvcontaining Apple stock prices data. See sample data section below for more details. Each column is separated by a tab.- You need
mpl_financePython package to draw candlestick chart. See here for instructions on how to installmpl_finance.
Installation
# Download PeakUtils zip file from https://bitbucket.org/lucashnegri/peakutils/downloads/ pip install lucashnegri-peakutils-XXXXXX.zip
Usage
Look at the code below at the Peak section. It is very simple to use the PeakUtils library.
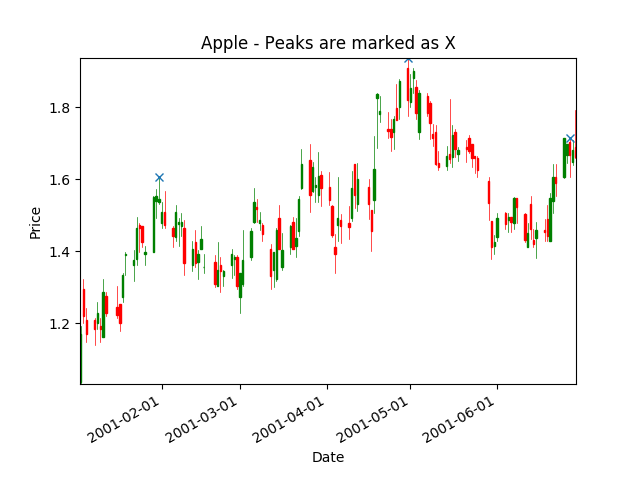
#!/usr/bin/python3 import matplotlib matplotlib.use('Agg') # Bypass the need to install Tkinter GUI framework # Avoid FutureWarning: Pandas will require you to explicitly register matplotlib converters. from pandas.plotting import register_matplotlib_converters register_matplotlib_converters() import pandas as pd from mpl_finance import candlestick_ohlc import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import matplotlib.dates as mdates import peakutils # Load data from CSV file. ########################## my_headers = ['date', 'open', 'high', 'low', 'close', 'volume'] my_dtypes = {'date': 'str', 'open': 'float', 'high': 'float', 'low': 'float', 'close': 'float', 'volume': 'int'} my_parse_dates = ['date'] loaded_data = pd.read_csv('apple.csv', sep='\t', header=1, names=my_headers, dtype=my_dtypes, parse_dates=my_parse_dates) # Convert 'Timestamp' to 'float'. # candlestick_ohlc needs time be in float days format - see date2num. loaded_data['date'] = [mdates.date2num(d) for d in loaded_data['date']] # Re-arrange so that each line contains values of a day: 'date','open','high','low','close'. quotes = [tuple(x) for x in loaded_data[['date','open','high','low','close']].values] # Plot candlestick. ########################## fig, ax = plt.subplots() candlestick_ohlc(ax, quotes, width=0.5, colorup='g', colordown='r'); # Peak ############ # Find peak points from high values. peak_indexes = peakutils.indexes(loaded_data['high'].values, thres=0.5, min_dist=30) peak_x = loaded_data['date'].values[peak_indexes] peak_y = loaded_data['high'].values[peak_indexes] plt.plot(peak_x, peak_y, "x") # Mark 'X' as peaks. # Customize graph. ########################## plt.xlabel('Date') plt.ylabel('Price') plt.title('Apple - Peaks are marked as X') # Format time. ax.xaxis_date() ax.xaxis.set_major_formatter(mdates.DateFormatter("%Y-%m-%d")) plt.gcf().autofmt_xdate() # Beautify the x-labels plt.autoscale(tight=True) # Save graph to file. plt.savefig('peak.png')
Chart output
apple.csv sample data
date open high low close volume 2001-01-02 1.062500 1.089286 1.040179 1.062500 113078000 2001-01-03 1.035714 1.191964 1.031250 1.169643 204268400 2001-01-04 1.295757 1.321429 1.200893 1.218750 184849000 2001-01-05 1.209821 1.241071 1.147321 1.169643 103089000 2001-01-08 1.209821 1.213164 1.138393 1.183036 93424800

