Overview
Here is a simple example showing how to use Tulip Indicators and Matplotlib to draw Moving Average Convergence/Divergence (MACD). The data used here is taken from https://tulipindicators.org/macd.
Requirement
- numpy, pandas, matplotlib, tulipy Python packages are installed on your system.
Code
#!/usr/bin/python3 import pandas as pd import tulipy as ti import matplotlib matplotlib.use('Agg') # Bypass the need to install Tkinter GUI framework import matplotlib.pyplot as plt # Avoid FutureWarning: Pandas will require you to explicitly register matplotlib converters. from pandas.plotting import register_matplotlib_converters register_matplotlib_converters() # Load data from CSV file. ########################## my_headers = ['date', 'price'] my_dtypes = {'date': 'str', 'price': 'float'} my_parse_dates = ['date'] # List columns that should be parsed as date. loaded_data = pd.read_csv('data.csv', sep='\t', header=None, names=my_headers, dtype=my_dtypes, parse_dates=my_parse_dates) # Plot the main graph. ########################## x = loaded_data['date'] y = loaded_data['price'] (fig, ax1) = plt.subplots() ax1.set_xlabel('Date') ax1.set_ylabel('Price ($)') lax1, = ax1.plot(x, y, color='black', label='Main graph') # Plot MACD. ########################## short_period = 2 long_period = 5 signal_period = 9 # Calculate MACD. macd_input=loaded_data['price'].values # Convert pandas dataframe to NumPy array. (macd, macd_signal, macd_histogram) = ti.macd(macd_input, short_period=short_period, long_period=long_period, signal_period=signal_period) macd_x = loaded_data['date'].values macd_x = macd_x[4:] # Skip 1st 4 due to long_period=5. ax2 = ax1.twinx() # Instantiate a second axes that shares the same x-axis ax2.set_ylabel('MACD value', color='red') ax2.tick_params(axis='y', labelcolor='red') # Draw macd values. lax2_m1, = ax2.plot(macd_x, macd, color='yellow', label='MACD') lax2_m2, = ax2.plot(macd_x, macd_signal, color='orange', label='MACD signal') lax2_m3, = ax2.plot(macd_x, macd_histogram, color='blue', label='MACD histogram') # Customize graph ########################## # Set graph labels & legend title='Draw MACD({}, {}, {}) on right axis \nusing Tulip Indicator & Matplotlib'.format( short_period, long_period, signal_period) plt.title(title) plt.legend([lax1, lax2_m1, lax2_m2, lax2_m3], ['Main graph', 'MACD', 'MACD signal', 'MACD histogram']) plt.gcf().autofmt_xdate() # Beautify the x-labels plt.autoscale(tight=True) # Save graph to file. plt.savefig('macd-right-axis-tulip-matplotlib.png')
Output chart
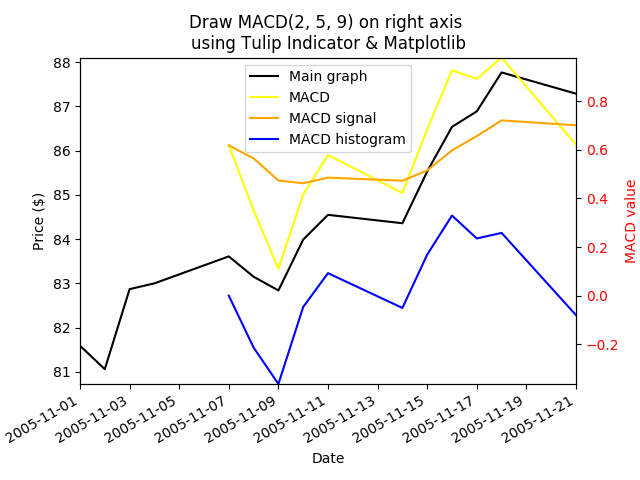
Input data: data.csv
2005-11-01 81.59 2005-11-02 81.06 2005-11-03 82.87 2005-11-04 83.00 2005-11-07 83.61 2005-11-08 83.15 2005-11-09 82.84 2005-11-10 83.99 2005-11-11 84.55 2005-11-14 84.36 2005-11-15 85.53 2005-11-16 86.54 2005-11-17 86.89 2005-11-18 87.77 2005-11-21 87.29

